Countless new products and medications hit stores’ shelves and doctors’ prescription pads every year. Many are a result of small tweaks to already available treatments. A select few, though, totally change the game: A preventative migraine drug slashes monthly headaches in half, an injectable gene restores sight to those with a degenerative eye condition, and a better-designed sunscreen helps more people keep damaging rays at bay. These 10 medical advances represent how science, technology, and creative thinking can help us live longer, better lives.
Aimovig by Amgen & Novartis

The first migraine-prevention drug
Twelve percent of people worldwide live with the pounding head pain and other debilitating effects of migraine. What’s worse? The drugs commonly used to prevent the attacks are meant for other ailments—high blood pressure, seizures, depression. These medicines don’t always work and often cause intolerable side effects. The newly-approved drug Aimovig is the first to prevent migraines by targeting a specific molecular interaction involved in the disorder. The medicine blocks a neurotransmitter called the calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP), which stimulates brain cells active in migraines. The monthly injection reduces the number of monthly migraine attacks by an average of 50 percent, with far fewer side effects.
Amgen
Black Girl Sunscreen SPF 30 Moisturizing Lotion by Black Girl Sunscreen

Finally, sunscreen designed for dark skin
Everyone who soaks up the sun needs skin protection. Yet, most sunscreens leave an undesirable white cast on darker skin that won’t fade until washed off with soap. Black Girl Sunscreen, though, is specifically designed for people of color. The FDA-approved product includes a blend of UVA- and UVB-fighting chemicals selected because their chemistry avoids that white residue. The lotion also contains multiple moisturizers to help prevent dry skin.
Black Girl Sunscreen
Abilify MyCite by Otsuka America Pharmaceutical & Proteus Digital Health

A pill that tells when it’s popped
As many as half of people who need daily medications don’t take their drugs on the prescribed schedule, which can reduce effectiveness. Technology incorporated in the antipsychotic medicine Abilify now lets physicians and patients track when meds go down. Once swallowed, embedded sensors in the high-tech drug—dubbed Abilify MyCite—generate an electrical signal that a band-aid-sized skin patch picks up and transmits to a nearby mobile device. Abilify MyCite is the first digital drug to gain FDA approval, but the sensor’s maker, Proteus Digital Health, plans to incorporate its device into other medicines, as well.
Proteus Digital Health
Luxturna by Spark Therapeutics

Replacing bad genes with good ones
In a group of inherited eye disorders collectively known as retinal dystrophy, faulty genes lead photoreceptors (retinal cells critical to vision) to slowly die over time, degrading sight. Luxturna is the first treatment for the condition, and also the first gene therapy to perform its cell modification within the body. It’s for people who have a mutation in a gene called RPE65 and consists of a benign virus that contains a healthy version of the gene. Treatment involves just one injection in each eye. After infusion, the virus ferries the gene into retinal cells. Then, a protein encoded by the gene restores the function of any remaining photoreceptors, thus slowing or stopping further vision loss. Researchers say Luxturna could pave the way for future treatments that deliver healthy genes into cells that lack them.
Spark Therapeutics
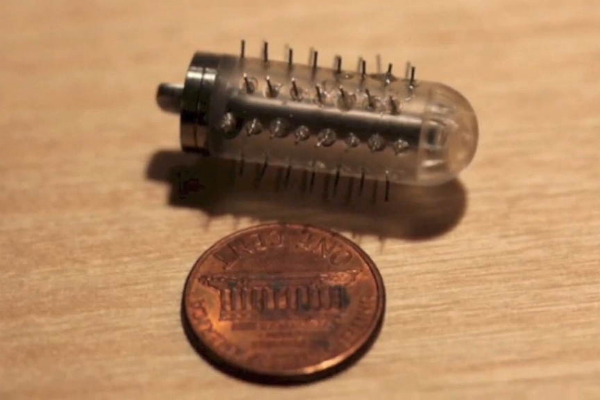
Confirm Rx insertable cardiac monitor by Abbott

Heart monitor the size of a paper clip
Abnormal heart rhythms known as arrhythmias, in which the ticker beats too fast or too slow, come with a risk for strokes and heart attacks. If a patient has suspicious symptoms, such as palpitations or fainting, a doctor will often test for an arrhythmia by having them wear an unwieldy device for a couple days to record the electrical signals that control heart contraction. Abbott’s Confirm Rx, a paper-clip-sized device inserted under the skin, makes the same measurements, but is much less onerous to patients. It continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity by performing a single-lead electrocardiogram, and it transmits the data via Bluetooth to the doctor for review.
Abbott
Eversense Continuous Glucose Monitoring System by Senseonics Holding

The three-month blood-sugar monitor
Many people with diabetes prick a finger several times a day to measure their blood-sugar (glucose) levels. They need the information to determine how much insulin to take to prevent levels from rising too high. Aside from being painful and annoying, finger sticks don’t track sugar between tests—a concern because chronically high levels can lead to heart disease, blindness, and kidney failure. Some existing devices avoid the bloodletting and measure glucose continuously for a week. But the Eversense Continuous Glucose Monitoring System does it for far longer: a full 90 days. The sensing component, which is about the size of a grain of rice, sits directly under the skin. It measures glucose every five minutes and sends the readings to a nearby mobile device for reference and storage.
Senseonics Holding
Apple Watch Series 4 by Apple
Arrhythmia-spotting smartwatch
Smartwatches can track your steps, count your pulse, and even guide you through a deep, relaxing breathe. Now, the Apple Watch has taken a giant leap forward in the medical sphere: The Series 4 can do an electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the electrical activity of the heart—a test usually performed in a doctor’s office. When you hold a finger firmly on the digital crown, conductors in the back of the watch and the circlet measure your heart’s electrical pulses and display the rhythm on-screen. Apple’s ECG is greenlit to detect a type of arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation (a condition in which the upper chambers of the heart tremble instead of beat, affecting blood flow). It’s not as powerful a test as those in doctors’ offices, and how well it stacks up against other arrhythmia detectors isn’t clear yet. However, its potential benefit to public health can’t be understated: In the future, if users can opt-in to sharing their data with research studies, it could help doctors identify early warning signs of the disease.
Apple
Butterfly iQ by Butterfly

Ultrasounds for everyone
Ultrasounds are incredibly useful: They allow physicians to visualize our internal organs, muscles, tendons, and even the blood vessels in our hearts. But the machines are also cumbersome and expensive. Costly piezoelectric crystals must be carefully incorporated into each probe, and different areas of the body require their own probes; a high-frequency ultrasound reaches shallow tissue just under the skin, while a low-frequency one visualizes tissue deep under the skin, like the heart muscle. The Butterfly iQ is different. Instead of a piezo crystal, the device uses a far cheaper silicon chip that can generate frequencies needed for any depth. This reduces the cost of an ultrasound machine from $40,000 or more to just $2,000, putting the purchase within reach of more physicians.
Butterfly
Shingrix by GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals

Surefire shingles vaccine
At some point in life, one in three Americans will suffer from shingles, a painful, itchy, and blistery rash that develops on one side of the body. Caused by the same virus as chickenpox in children, the rash usually resolves over a few weeks. Other times, though, it can cause pain in the affected area that persists for months or years. And, in rare cases, it can also lead to hearing and vision loss and strokes. The sole vaccine that was available until recently prevented the condition only about half the time. Late last year, though, the FDA approved Shingrix, a vaccine that prevents the rash in 90 percent of recipients in the first year and still works in 85 percent of patients four years later. Shingrix consists of a protein found on the virus’s surface and a substance that enhances immune responses; when the immune system “sees” the protein, it seeks out and attacks the virus itself, preventing trouble.
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Biktarvy by Gilead Sciences

The most-potent HIV drug yet
People infected with HIV, a type of retrovirus, must adhere strictly to treatment with antiretrovirals to avoid AIDS, the stage of infection that severely hampers the immune system’s ability to fight other attackers. This year, the FDA approved the most-potent therapy yet. Brand-named Biktarvy, the once-daily pill contains three drugs that tamp the virus in different ways, and together are more effective than they would be as solo treatments. One ingredient in particular, Bictegravir, is entirely new, and recent studies show it to be at least as effective as other anti-HIV retro virals on the market, with fewer side effects. It blocks one of the HIV proteins that plays a key role in spreading the virus throughout the body, and Bictegravir’s distinctive structure also minimizes unwanted interactions with other drugs.